Once the transformer has been installed and all fixture locations determined, the next step is to run the correct size cable from the transformer to the fixtures. LED fixtures should be provided between 10 and 15 volts AC. This is accomplished by:
- Grouping fixtures into distance zones as illustrated below. Do not have a fixture that is 10’ away from the transformer on the same cable run as one that is 100’ away.
- Use the proper cabling method for the application. Try to center load all cable runs when possible to minimize the voltage differential between fixtures.
- Use the correct size cable to accommodate voltage drop. As a general rule of thumb, limit the wattage load per each cable run to no more than 100 to 160 watts.
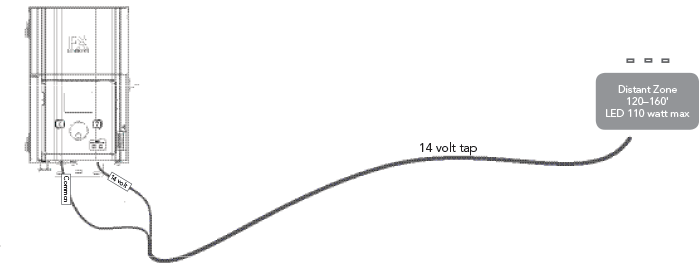
Watts shown are per 12 gauge cable. Install additional cable runs as needed to complete project. To increase wattage maximum, run 8 gauge or double 12 gauge to the first fixture in the zone. Use a digital voltmeter to fine tune circuits.
Summary: For maximum light output and lamp life, each lamp should be provided with between 10 to 15 volts AC. To stay within a 0.5 to 1.0 volt differential between the first light and the last light on a given circuit (while LED lights can support several volts of difference, good design practice is to minimize the voltage difference), you must group the fixtures into distance zones and not overload the cable with excessive wattage. As a rule of thumb, limit the distance between the first fixture and the last fixture on any given run to no more than 50 feet.
Note: Assign all FX ZD fixtures a group number prior to installation. If you are installing the Wi-Fi module and using the LAM, the group numbers for fixtures can be assigned after installation.
LED Wattage Equivalent Chart
| |
| Specifications |
1LED |
3LED |
6LED |
9LED |
ZDC |
| Halogen Lumen Output Equivalent |
10 watt |
20 watt |
35 watt |
50 watt |
20 watt |
| VA Total |
2.4 |
4.5 |
13.5 |
13.5 |
11.0 |