Within each cabling zone, you may utilize any of a number of cabling methods. The primary objective is to minimize voltage drop by installing the proper size feeder cable (home run) to each zone and to make sure that each fixture on each cable run is receiving between 10.5 and 11.5 volts, or 10–15 volts for LED fixtures. Center feeding the “home run” (the main cable run from the transformer to the first fixture on the circuit) will help minimize the voltage differential between the first fixture and the last fixture on the cable run.
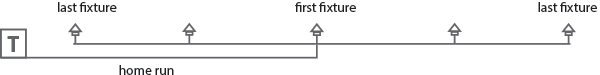
Tee method (Recommended for Incandescent systems)
The tee method center feeds the “home run” section of the cable and reduces the voltage differential between the first fixture and the last fixture on either side of the “tee.” This method is the preferred circuiting technique as it is easy to install and minimizes the voltage drop between first and last fixtures.
Daisy chain method (Recommended for LED systems)
Daisy chained circuits are the least efficient cabling method as more voltage is fed to the first fixture on the run and due to voltage drop, each subsequent fixture receives less and less voltage. This is not a problem for FX LED fixtures due to its large voltage acceptance range of 10–15 volts.